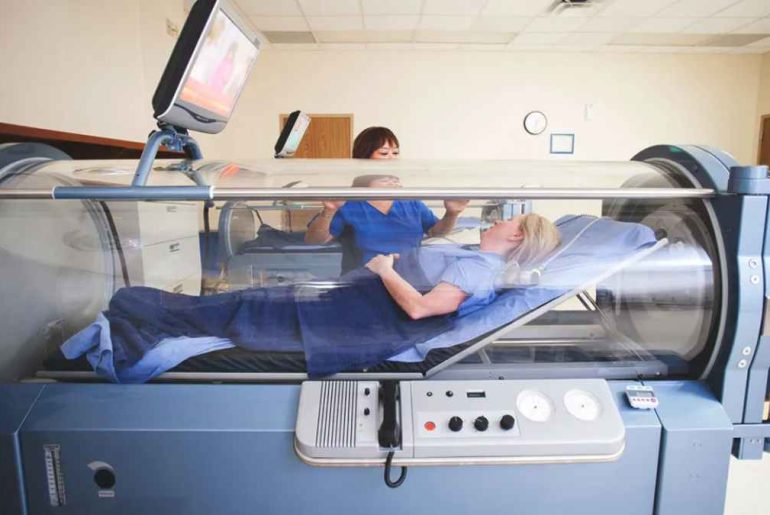
Oxygen therapy is prescribed for people who can’t get enough oxygen because of certain diseases and conditions. For example, McKinney oxygen therapy can benefit patients with lung conditions such as asthma, pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibroids, heart failure, and lung disease. Many patients receiving oxygen therapy often see improved energy levels, sleep, and quality of life. Oxygen therapy also reduces fatigue, headaches, irritability, and swollen ankle symptoms.
What happens during oxygen therapy?
You may be started on oxygen therapy immediately during emergency cases such as a possible heart attack, serious accident, or any other life-threatening event. During your hospital stay, your doctor, nurse, or respiratory therapist ensures you get the right amount of oxygen. If you have therapy at home, your home equipment provider will help you set up the necessary equipment at your house.
Guidelines for using oxygen therapy
Once your physician has issued a prescription for oxygen therapy, they will guide you on how and when to use it. You’ll be informed of the flow rate that’s necessary for each minute of usage. If there are difficulties encountered with using the treatment, make sure to seek medical attention before making any modifications.
Supplemental oxygen requirements vary from person to person; some only need oxygen when exercising or sleeping, while others need oxygen throughout. Most types of oxygen therapy have portable oxygen tanks which you can carry when necessary.
To get the most out of oxygen therapy, it is essential to avoid drinking alcohol or using any illicit substances. Additionally, make sure you communicate with your doctor about all prescription medications that you are taking before starting this treatment. This way they can ensure that the oxygen therapy will be effective and safe for you!
What are the potential risks of oxygen therapy?
Supplemental oxygen therapy is generally safe but can cause side effects such as dry or blood nose fatigue and morning headaches. The nasal cannula or face mask can also cause skin irritation. If these problems persist, inform your home equipment provider and your doctor. Depending on the issue, your doctor may need to change your oxygen flow rate or duration.
If you have a dry nose, your healthcare provider recommends a nasal spray or adding a humidifier to your oxygen equipment. For an uncomfortable face mask or nasal cannula, your provider can help you find a device with a better fit. You can also use over-the-counter gels and devices to reduce skin irritation.
Transtracheal oxygen therapy can result in more serious complications. For this type of oxygen therapy, oxygen gas is delivered into your windpipe through the front of your neck. Possible complications of transtracheal oxygen therapy include infection and injury to the lining of the windpipe. The tube can also slip or break, and mucus balls may develop on the tube inside the windpipe. The formation of mucus balls can cause coughing and clogging of the windpipe.
Oxygen gas is not explosive but supports combustion and can worsen a fire. In the presence of oxygen gas, a small fire can get out of control in no time.
Request an appointment with your doctor at Kurv O2 to know how you can benefit from oxygen therapy.